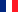
The NutriNet-Santé study was set up to investigate nutrition and health relationships. Specifically, it was the first web-based cohort worldwide on such a large scale (n=164 000 as of 2019) focused on the complex link between nutrition and health status. It is characterized by a very detailed assessment of nutritional exposure and dietary behavior. A biobank comprising samples of serum, plasma, and buffy-coats for genetic analyses, as well as urine samples was set up for 19 600 subjects of the cohort. It represents a unique platform for establishing multidisciplinary research projects and collaborations, with the capability and flexibility to add ancillary protocols and questionnaires and thus rapidly collect large amounts of high-quality data. Our ambition is to expand NutriNet-Santé to other countries. It has already been launched in Belgium and pilot studies are ongoing in Switzerland, Spain, Canada and Mexico. Our team is a pioneer of e-epidemiology at the international level having conducted numerous methodological research investigations in this field.
EREN was the first research team in France to obtain authorization by the State Council (in 2012) to link data from our cohorts with data from the national health insurance system (which includes detailed information on prescription medication use, sick leaves, etc). In addition to augmenting our databases, such access allows us to set up specific programs focused on long-term drug use in interaction with nutrition.
Go to Etude-Nutrinet-Santé
See also the Nutrinet-Santé institutional website






 The "Supplementation en VItamines et Minéraux AntioXydants" (SU.VI.MAX) Study is a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, primary-prevention trial designed to test the efficacy of a daily supplementation with antioxidant vitamins and minerals, in reducing cancer and ischaemic vascular disease incidence in a general population. 14,412 subjects living in France (women aged 35 to 60, and men 45 to 60) were selected from 79,976 volunteers enrolled after a five-month (March-July 1994) national multimedia campaign. Of these subjects 13,017 were assigned at random to one of two groups. Immediately after randomisation, 270 subjects declared that they were no longer willing participate in the study and 6 subjects were recognised as ineligible (out of the age range after verification). Supplementation consisted to a combination of 120 mg vitamin C, 30 mg vitamin E, 6 mg beta-carotene, 100 µg selenium (as selenium-enriched yeast) and 20 mg zinc (as gluconate); or a matching placebo in a single daily capsule. At enrolment and at 12-18 months intervals, participants were invited to visit a mobile medical unit or a preventive health center. Subjects were asked to complete a monthly questionnaire, summarising treatment compliance and health events, via Minitel (a phone-based French terminal), the internet or mail. Primary outcomes were major ischaemic events (ICD codes 120-124) and cancer of any kind, except for basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Secondary outcome was all-cause mortality. After a median follow-up time of 7.5 years, intention-to-treat comparisons were performed between both groups.
The "Supplementation en VItamines et Minéraux AntioXydants" (SU.VI.MAX) Study is a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, primary-prevention trial designed to test the efficacy of a daily supplementation with antioxidant vitamins and minerals, in reducing cancer and ischaemic vascular disease incidence in a general population. 14,412 subjects living in France (women aged 35 to 60, and men 45 to 60) were selected from 79,976 volunteers enrolled after a five-month (March-July 1994) national multimedia campaign. Of these subjects 13,017 were assigned at random to one of two groups. Immediately after randomisation, 270 subjects declared that they were no longer willing participate in the study and 6 subjects were recognised as ineligible (out of the age range after verification). Supplementation consisted to a combination of 120 mg vitamin C, 30 mg vitamin E, 6 mg beta-carotene, 100 µg selenium (as selenium-enriched yeast) and 20 mg zinc (as gluconate); or a matching placebo in a single daily capsule. At enrolment and at 12-18 months intervals, participants were invited to visit a mobile medical unit or a preventive health center. Subjects were asked to complete a monthly questionnaire, summarising treatment compliance and health events, via Minitel (a phone-based French terminal), the internet or mail. Primary outcomes were major ischaemic events (ICD codes 120-124) and cancer of any kind, except for basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Secondary outcome was all-cause mortality. After a median follow-up time of 7.5 years, intention-to-treat comparisons were performed between both groups. Study involving a cohort of adults who were enrolled in the initial SU.VI.MAX trial (a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial launched in 1994 to test the impact of daily nutritional doses of anti-oxidant vitamins and minerals administrated over 8 years). The main objective of the SU.VI.MAX2 study was to investigate the relationships between overall dietary behaviours (dietary patterns) and/or specific nutritional factors (intake or blood concentrations of anti-oxidants, folate, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), protein and energy intake) and quality of aging. The exposure variables were estimated from data collected during 1994-1996 (eg, baseline SU.VI.MAX data). The aging outcomes were evaluated 10-12 years later (2007-2009). Using self-administrated questionnaires and clinico-biological examinations, we collected information on cognitive function, mood, wellbeing, social integration, nutritional status, bone health, balance impairment, sensory problems, physical performance and mobility and prevalent diseases. Neuro-psychological examinations were performed by health professionals recruited specifically for this purpose.
Study involving a cohort of adults who were enrolled in the initial SU.VI.MAX trial (a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial launched in 1994 to test the impact of daily nutritional doses of anti-oxidant vitamins and minerals administrated over 8 years). The main objective of the SU.VI.MAX2 study was to investigate the relationships between overall dietary behaviours (dietary patterns) and/or specific nutritional factors (intake or blood concentrations of anti-oxidants, folate, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), protein and energy intake) and quality of aging. The exposure variables were estimated from data collected during 1994-1996 (eg, baseline SU.VI.MAX data). The aging outcomes were evaluated 10-12 years later (2007-2009). Using self-administrated questionnaires and clinico-biological examinations, we collected information on cognitive function, mood, wellbeing, social integration, nutritional status, bone health, balance impairment, sensory problems, physical performance and mobility and prevalent diseases. Neuro-psychological examinations were performed by health professionals recruited specifically for this purpose.
 Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled secondary prevention clinical trial with cardiovascular disease (CVD) survivors (N=2,501; aged 45-80 years). It employed a 2x2 factorial design (4 possible combinations) as well as B vitamins and n-3 PUFA delivered at nutritional doses. Specifically, individuals who had experienced a myocardial infarction (MI), an acute coronary attack without necrosis or an ischemic stroke in the 1 to 12 months prior to their enrolment in the study were randomly allocated to one of the 4 possible combinations:
Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled secondary prevention clinical trial with cardiovascular disease (CVD) survivors (N=2,501; aged 45-80 years). It employed a 2x2 factorial design (4 possible combinations) as well as B vitamins and n-3 PUFA delivered at nutritional doses. Specifically, individuals who had experienced a myocardial infarction (MI), an acute coronary attack without necrosis or an ischemic stroke in the 1 to 12 months prior to their enrolment in the study were randomly allocated to one of the 4 possible combinations: